Clean filter effectively captures dust, pollen, mold spores, pet dander, and other airborne particles, promoting unrestricted airflow for optimal HVAC system performance and energy efficiency. This results in improved indoor air quality, creating a healthier living environment.
A dirty air filter becomes less effective in capturing particles as it collects dirt and debris, allowing more contaminants to circulate. This reduced efficiency leads to restricted airflow, making the HVAC system work harder to maintain the desired temperature and causing increased energy consumption and higher utility bills. Prolonged use of a dirty filter poses the risk of potential damage to HVAC system components over time, highlighting the importance of regular maintenance.

An air filter functions as a screen designed to fit into the HVAC system’s compartment, purifying the air as it circulates within a home. These filters are typically an aftermarket product and have a lifespan ranging from 1 to 6 months for disposable variants. Washable air filters, on the other hand, can endure for up to five years.
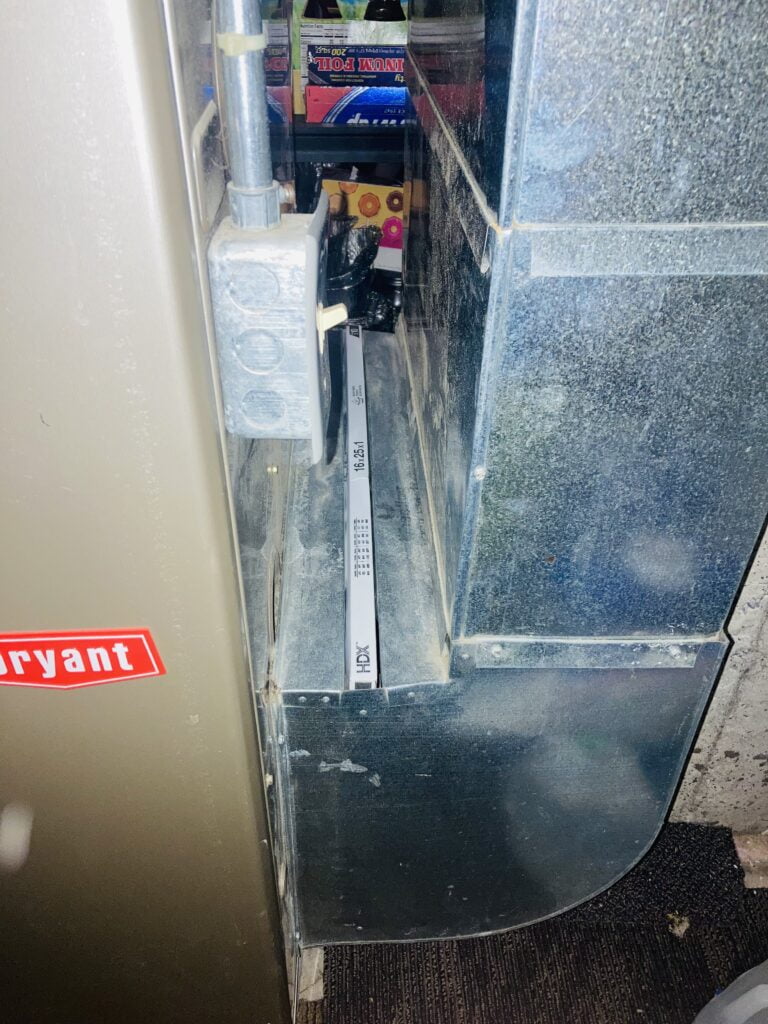
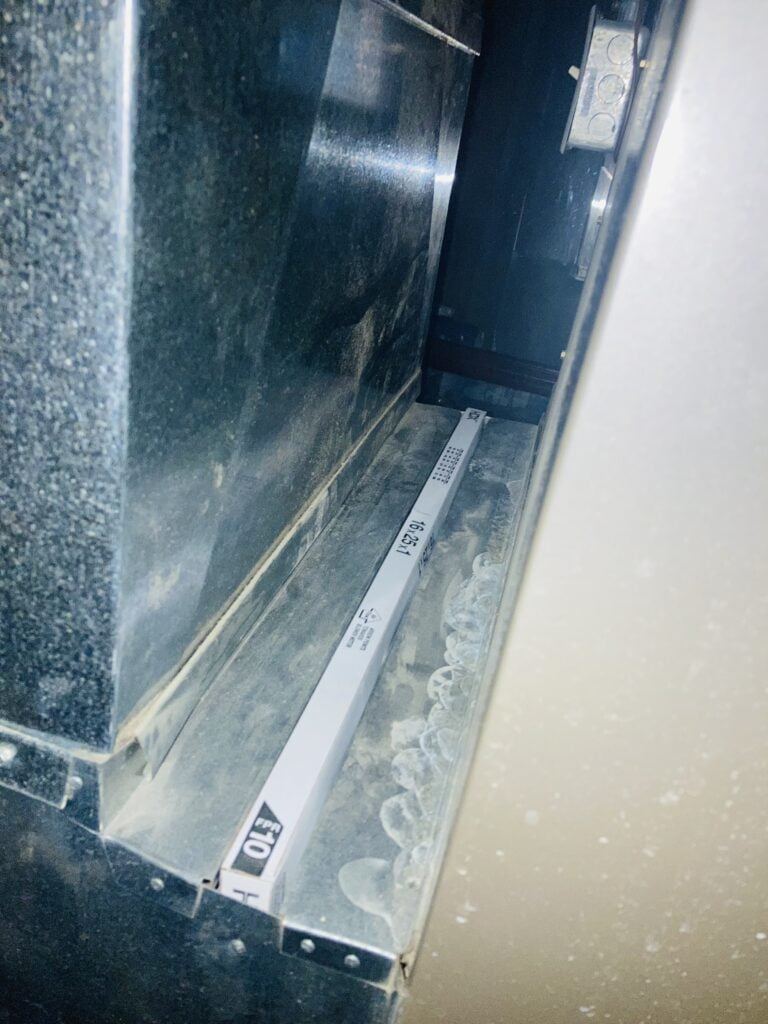


Quick guide to Locating your Air Filter in your house:
Air filters are commonly located between the return duct and the air handler. If you still have not found your air filter or furnace filter, look between the return duct and the air handler. The air handler is a large metal box that houses the fan and its motor.
A home air filter is a device designed to remove particles and pollutants from the air in your home. It is typically installed in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system to help improve indoor air quality. The filter traps various airborne contaminants such as dust, pollen, pet dander, mold spores, bacteria, and other particles. This can be especially beneficial for people with allergies or respiratory conditions, as it helps to reduce the concentration of allergens in the air.
Easy steps in Replacing you Furnace Dirty Air filter
- Turn off the power:
- Locate the electrical panel and turn off the power to the existing furnace.
- Turn off the gas supply:
- Shut off the gas supply to the furnace. This usually involves turning the gas valve to the “off” position.
- Disconnect utilities:
- Disconnect the gas line, electrical wiring, and any other utilities connected to the old furnace.
- Remove the old furnace:
- Disconnect the ductwork attached to the furnace.
- Loosen and disconnect the old furnace from its mounting brackets or platform.
- Carefully remove the old furnace from its location.
- Prepare the new furnace:
- Ensure the new furnace is the correct size and type for your home.
- Check that the new furnace meets local building codes and regulations.
- Install the new furnace:
- Position the new furnace on its mounting brackets or platform.
- Connect the ductwork to the new furnace.
- Connect the gas line and ensure all connections are secure.
- Connect the electrical wiring following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Test the new furnace:
- Turn on the power and gas supply.
- Test the furnace by running it through a heating cycle.
- Check for any unusual noises, smells, or performance issues.
- Adjust settings:
- Set the thermostat to the desired temperature.
- Adjust any settings on the new furnace as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Check for leaks:
- Inspect for gas or air leaks around the connections.
- Use a gas leak detector solution to check for gas leaks.
- Secure permits and inspections:
- Check with your local authorities to see if you need permits for the installation.
- Schedule an inspection to ensure the installation meets safety and building code standards.
Remember, furnace replacement can be a hazardous task, and it’s crucial to prioritize safety. If you are not comfortable or familiar with the process, it’s strongly recommended to hire a licensed HVAC professional for the job.
Types of home air filters, each with varying levels of filtration efficiency
- Mechanical Filters: These filters physically trap particles as air passes through them. They include:
- Fiberglass Filters: These are relatively inexpensive and have a low efficiency rating. They’re primarily designed to protect the HVAC system itself rather than improve indoor air quality significantly.
- Pleated Filters: These have a larger surface area and higher efficiency compared to fiberglass filters. They can capture smaller particles.

2.High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) Filters: These are extremely efficient mechanical filters capable of capturing particles as small as 0.3 micrometers with a high degree of effectiveness. These Air filter are use a lot in health Care settings. During the the Covid Pandemic these filters were in high demand and was use during care of Infected Patient.
3. Electrostatic Filters: Electrostatic filters , also known as Washable air filters , offer a reusable and durable alternative to standard disposable furnace filters. These filters, such as the ones manufactured by Air Filters, Inc., are up to 10 times more efficient. The reusable Life Time Filter, in particular, can trap up to 94% of dust and allergens, thanks to its electrostatic charge generated by the friction of air movement, known as Static Cling. This charge causes dirt and dust to adhere to the filter, maintaining cleaner equipment coils and optimal operational capacity without incurring additional electrical costs. These use an electrostatic charge to attract and trap particles. They can be either washable and reusable or disposable.

washable filter
4. Activated Carbon Filters: These are effective at removing odors, chemicals, and gases from the air. They work by adsorbing (not absorbing) these substances onto the surface of the carbon.
5. UV Filters (Ultraviolet): These use ultraviolet light to kill or deactivate bacteria, viruses, and mold spores that pass through the filter.
6.Ozone Generators: These devices release ozone into the air, which can help eliminate odors and some pollutants. However, they can be harmful to humans and pets if not used properly.
It’s important to regularly replace or clean the filter according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure it continues to work effectively. Neglecting to do so can reduce its efficiency and potentially strain your HVAC system.
Selecting the right type of filter for your home depends on factors like the specific pollutants you’re trying to address, the size of particles you want to filter, and your budget. Consulting with an HVAC professional or referring to your system’s user manual can help you choose the most appropriate filter for your needs.
Advantages and Benefits of a clean HVAC home Filter.
1.Improved Air Quality: The primary purpose of an air filter is to remove particles and contaminants from the air. A clean air filter ensures that the air circulating in your home is free from dust, pollen, mold spores, pet dander, and other allergens. This is especially important for individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions.
2. Enhanced HVAC Efficiency: In a heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system, a clean air filter allows for better airflow. When air flows freely through the system, it doesn’t have to work as hard to maintain the desired temperature, which can result in lower energy bills.
3. Extended Equipment Life: A clean air filter helps prevent dust and debris from accumulating on sensitive components of your HVAC system or vehicle engine. This reduces wear and tear, which can extend the lifespan of the equipment and reduce the likelihood of expensive repairs.
4.Improved Fuel Efficiency: In a vehicle, a clean air filter allows for better air intake, which is crucial for combustion. When the engine receives clean air, it can operate more efficiently, potentially leading to better fuel economy.
5.Reduced Emissions: When an engine has a clean air filter, it can burn fuel more efficiently. This means it emits fewer pollutants into the air, contributing to a cleaner environment and potentially complying with emissions regulations.
6. Prevention of Icing and Freezing: In HVAC systems, a clean air filter helps prevent the coils from becoming clogged with debris. This reduces the risk of ice forming on the coils, which can lead to reduced efficiency and potential damage .
7. Maintains Consistent Airflow: Clean air filters ensure a consistent flow of air through the system, which helps maintain a comfortable indoor environment. This is important for maintaining a stable temperature and humidity level.
8. Reduces Strain on the System: A dirty or clogged air filter forces the system to work harder to draw in air. This increased strain can lead to overheating, decreased performance, and potential system failures.
9.Lower Maintenance Costs: Regularly changing or cleaning air filters is a relatively low-cost maintenance task that can prevent more costly repairs down the line. Neglecting to do so can lead to expensive repairs or even the need for a complete system replacement.
10.Improved Respiratory Health: In homes, clean air filters can significantly benefit individuals with respiratory conditions like asthma or allergies. They help remove irritants and allergens from the air, creating a healthier living environment.
Video Compliments The Air Of Authority
How Dose an Air filter works:
- Physical Barrier: Most air filters operate on the principle of a physical barrier. The filter is made of a porous material that allows air to pass through while trapping particles. The material can be made of fibers, paper, fiberglass, foam, or other synthetic materials.
- Particle Capture: As air passes through the filter, particles in the air collide with the fibers or other filtering media. The larger particles are unable to navigate through the small openings between the fibers and are thus captured by the filter.
- Filter Efficiency: The effectiveness of an air filter is often measured by its efficiency in capturing particles of various sizes. Filters are assigned a Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value (MERV) rating, which ranges from 1 to 16 (higher values indicate higher efficiency). The MERV rating indicates the filter’s ability to capture particles of different sizes, with higher MERV ratings being more effective at trapping smaller particles.
- Types of Filters:
- Fiberglass Filters: These are relatively inexpensive and common in residential HVAC systems. They are suitable for capturing larger particles but may not be as effective for smaller particles.
- Pleated Filters: These filters have more surface area due to their folded design, providing better particle capture efficiency.
- High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) Filters: HEPA filters are extremely efficient and can capture very small particles, including allergens and some viruses. They are commonly used in air purifiers and certain industrial settings.
- Regular Replacement: Over time, air filters accumulate captured particles, reducing their effectiveness. It’s essential to regularly replace or clean filters to maintain optimal performance and prevent airflow restriction.
Several ways in which air filters clean the air
- Mechanical Filtration: This is the most common type of air filtration. It uses a physical barrier (the filter) to trap particles as air passes through. The filter material has small pores that allow air to pass but capture particles.
- Fiber Filters: These filters use layers of fibers to capture particles. The density, thickness, and material of the fibers determine the filter’s efficiency.
- Activated Carbon Filters: These filters are coated with a layer of activated carbon. Activated carbon is highly porous and can absorb odors, gases, and chemicals in the air.
- HEPA Filters: High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters are extremely effective at capturing very small particles. To qualify as a HEPA filter, it must remove at least 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 micrometers in diameter.
- Electrostatic Filters: These filters use an electrostatic charge to attract and trap particles. They can be either disposable or washable.
- UV Filters: Some air filtration systems incorporate ultraviolet (UV) light to kill or inactivate bacteria, viruses, and mold spores. This is often used in combination with other filtration methods.
- Ozone Generators: While not technically a filter, ozone generators release ozone molecules into the air. Ozone can react with pollutants and neutralize them. However, it’s important to note that high levels of ozone can be harmful to human health.
- Photocatalytic Oxidation (PCO) Filters: PCO filters use a combination of UV light and a catalyst to break down and neutralize organic compounds, bacteria, and viruses.
- Ionic Filters: These filters use charged ions to attract and capture particles. They can be effective, but some studies suggest they may produce harmful ozone as a byproduct.
- Molecular Sieve Filters: These filters are designed to capture and remove specific gases or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from the air.
- Pre-Filters: Many air filtration systems have a pre-filter that captures larger particles like dust, hair, and pet dander before the air reaches the main filter.
- Antimicrobial Filters: These filters are treated with an antimicrobial agent that inhibits the growth of bacteria, mold, and other microorganisms.
Remember that different filters have different levels of efficiency and are designed for specific purposes. It’s important to choose a filter that suits your specific needs and to replace or clean it regularly to maintain its effectiveness. Additionally, the MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value) rating is a good indicator of a filter’s efficiency. Higher MERV ratings indicate better filtration.
Illnesses prevented by clean Air filter
- Respiratory Infections: Clean air filters can remove bacteria and viruses from the air, reducing the risk of respiratory infections like the flu and common cold.
- Asthma and Allergies: They can trap allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold spores, which can exacerbate asthma and allergy symptoms.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Clean air filters can remove fine particles and pollutants that can aggravate symptoms and worsen the condition for individuals with COPD.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Fine particulate matter and pollutants in the air have been linked to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems. Clean air filters can help reduce exposure to these harmful substances.
- Lung Cancer: Long-term exposure to certain air pollutants has been associated with an increased risk of lung cancer. Clean air filters can help reduce this risk by removing carcinogenic particles.
- Bronchitis: Clean air filters can help prevent acute and chronic bronchitis by reducing exposure to irritants and pollutants that can inflame the bronchial tubes.
- Pneumonia: By reducing the presence of bacteria and viruses in the air, clean air filters can help lower the risk of contracting pneumonia.
- Sinusitis: Allergens and pollutants in the air can irritate the sinuses and contribute to the development of sinusitis. Clean air filters can help mitigate this risk.
- Headaches and Fatigue: Poor air quality can lead to headaches, fatigue, and a general feeling of malaise. Clean air filters can improve air quality and contribute to a healthier, more energetic environment.
- Skin Irritations: Airborne particles and allergens can contribute to skin irritation and conditions like eczema. Clean air filters can help reduce exposure to these irritants.
- Eye Irritations: Allergens and pollutants in the air can irritate the eyes, leading to symptoms like redness, itching, and watering. Clean air filters can help alleviate these issues.
- Neurological Effects: Some studies suggest that exposure to certain air pollutants may have negative effects on the nervous system. Clean air filters can help reduce this risk.
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)When appropriately employed, air purifiers and HVAC filters play a crucial role in diminishing airborne pollutants, including viruses, within enclosed spaces. However, it’s important to note that relying solely on air purification or filtration is insufficient in safeguarding against COVID-19. When integrated with other recommended measures from organizations like the CDC, such as maintaining social distance and wearing masks, filtration becomes an integral component of a comprehensive strategy to mitigate the risk of indoor airborne transmission of COVID-19.
It’s important to note that while clean air filters can significantly improve indoor air quality and reduce the risk of these illnesses, they are just one component of a comprehensive approach to maintaining good health.
Color Coded Grade for Standard pleated furnace Air Filter
Furnace Air Filter are color coded to show the grade of quality and protection offer for example in my picture below.



these are color coded air filter to Choose from depends on the protection you want.

wide variety and sizes of Air filter
Green

This Grade filters Dust/Lint ,pet dander, pollen , Airborne dust mite debris. It is considered GOOD with a FPR (Filter Performance Rating) of 4-5.
Red

This Grade Filters Dust/lint, Pet dander ,pollen, Airborne dust mite debris, mold spores, bacteria. It is considered BETTER with a FPR (Filter Performance Rating) of 6-7.
Purple

This Grade Filters Dust/lint, Pet dander, pollen, Airborne dust mite debris, mold spores, bacteria, microscopic allergen, Virus Carrier, most smoke. It is considered BEST with a FPR (Filter Performance Rating ) of 8-9.
Black

Easy General steps you can follow to clean a Dirty air filter.
Cleaning an air filter is an essential part of maintaining good air quality in your home or vehicle. Here are some general steps you can follow to clean an air filter:
Materials Needed:
- Screwdriver (if necessary)
- Vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment
- Water (for washable filters)
- Mild detergent (for washable filters)
- Bucket (for washable filters)
- Towel or paper towels
- Read the Manual: Always refer to the manufacturer’s manual for specific instructions and guidelines for your particular air filter. Different filters may have unique requirements.
- Turn Off the Device: Before attempting to clean the air filter, make sure to turn off the device to ensure your safety and prevent any damage to the equipment.
- Locate the Air Filter: Identify the location of the air filter in your device. It’s usually behind a cover or grille, and in some cases, you may need to use a screwdriver to open the compartment.
- Remove the Filter: Take out the air filter from its housing. Be gentle to avoid damaging any components.
- Inspect the Filter: Examine the filter for visible dirt, dust, or debris. If it’s heavily soiled or damaged, you might need to replace it rather than clean it.
- Vacuum or Brush: For light dirt and dust buildup, you can use a vacuum cleaner with a soft brush attachment to gently remove debris. Ensure that you vacuum both sides of the filter.
- Rinse with Water (if applicable): Some filters can be rinsed with water. If your filter is washable, rinse it under cool, running water. Use a gentle stream to avoid damaging the filter. Do not use hot water, as it can damage certain types of filters.
- Allow to Dry: After rinsing, allow the filter to air-dry completely before reinserting it into the device. Ensure it’s thoroughly dry to prevent mold or mildew growth.
- Reinstall the Filter: Once the filter is clean and dry, place it back into the device. Ensure it is properly seated and secured.
- Reset or Replace the Filter Indicator (if applicable): If your device has a filter replacement indicator, reset it according to the manufacturer’s instructions or replace the filter if necessary.
- Dispose or Store the Waste: If you’ve replaced the filter, follow proper disposal procedures. If you’ve cleaned a reusable filter, store any tools used for cleaning and dispose of any debris properly.
6 easy steps to clean A dirty Washable Air Filters:
- Turn Off the System: Before you begin, make sure to turn off the system that uses the filter. This could be your air conditioner, furnace, or ventilation system.
- Remove the Filter: Take out the filter from its housing. Refer to the owner’s manual if you’re unsure how to do this.
- Vacuum: Use a vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment to gently remove large debris, dust, and dirt from the filter. Be careful not to damage the filter during this process.
- Wash the Filter (if applicable): If your filter is washable, fill a bucket with water and add a mild detergent. Gently agitate the filter in the water to remove dirt and grime. Rinse thoroughly with clean water.
- Dry the Filter: Allow the filter to air dry completely before reinstalling it. Make sure it’s completely dry to prevent mold or mildew growth.
- Reinstall the Filter: Put the clean and dry filter back into its housing. Ensure it’s properly seated.
Fast & Easy Steps to Clean A Disposable Dirty Air Filters
- Turn Off the System: Again, ensure the system is turned off before starting.
- Remove the Filter: Take out the disposable filter. Most disposable filters don’t need to be cleaned; they should be replaced.
- Inspect the Filter: If the filter looks excessively dirty or damaged, it’s time for a replacement.
- Dispose or Replace: If it’s a disposable filter, dispose of it properly and replace it with a new one. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific system.
Remember to check your air filter regularly, especially during peak usage times, and replace or clean it as needed. This helps maintain good air quality and ensures your HVAC system runs efficiently.
Common Causes of Dirty Air Filter
A dirty air filter is like a silent defender in our homes and offices. It sits inside our HVAC systems, working hard to catch dust, allergens, and pollutants and keep our indoor air clean. Over time, it gets covered in dirt, making it less effective. Even though it quietly asks for attention, ignoring it can have big consequences. It’s crucial to grasp the importance of this simple component, as it plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy and breathable environment.

A dirty air filter can be caused by various factors, and it’s essential to address these issues promptly to maintain optimal air quality and HVAC system performance.
list of common causes of a dirty air filter:
- Lack of Regular Maintenance: Neglecting regular maintenance is one of the primary causes of a dirty air filter. Filters should be checked and replaced or cleaned according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- High Pollutant Levels: If the environment is particularly dusty or there are high levels of airborne particles (e.g., construction sites, industrial areas), the filter can get dirty more quickly.
- Pet Dander and Hair: If you have pets, their dander and hair can accumulate in the filter, especially if the pets shed a lot.
- Cigarette Smoke: Smoking indoors can lead to a rapid buildup of particles in the air filter.
- Pollen and Outdoor Allergens: During certain times of the year, pollen levels can be high, and this can contribute to a faster accumulation of particles in the filter.
- Mold and Mildew: In areas with high humidity levels or water damage, mold spores can become airborne and get trapped in the filter.
- Improper Ventilation: Inadequate ventilation in a space can lead to a higher concentration of pollutants and particles, putting more strain on the filter.
- Proximity to Construction or Industrial Sites: If your home or office is near construction sites or industrial areas, there may be higher levels of dust and particulate matter in the air.
- Faulty Ductwork: Leaky or damaged ductwork can introduce contaminants into the system, bypassing the filter altogether.
- Smog and Air Pollution: Living in an area with high levels of air pollution can lead to a quicker buildup of particles in the filter.
- Fireplaces and Wood-burning Stoves: Using a fireplace or wood-burning stove without proper ventilation or filtration can introduce soot and particulate matter into the air.
- Inadequate Sealing: Poorly sealed windows and doors can allow outdoor air (and its associated pollutants) to enter the indoor environment.
- Frequent Use of Scented Products: Using air fresheners, candles, or other scented products can release particles into the air that can clog the filter.
- Lack of Proper Filtration: Using a low-quality or incorrect type of filter for your HVAC system can lead to faster accumulation of dirt and debris.
- Pets or Wildlife in HVAC Unit: In some cases, animals may find their way into the HVAC system and contribute to filter contamination.
Regularly inspecting and replacing air filters, and addressing the underlying causes of filter dirtiness, is crucial for maintaining a healthy indoor environment and ensuring the efficiency of your HVAC system.

Dirty Air Filter
Negative Consequences of a Dirty Air Filter
- Reduced Airflow: A dirty air filter restricts the flow of air into your HVAC system. This means that your system has to work harder to pull in air, which can lead to decreased airflow throughout your home.
- Decreased Efficiency: When your HVAC system has to work harder to pull in air due to a dirty filter, it consumes more energy. This can result in higher energy bills.
- Poor Indoor Air Quality: The primary purpose of an air filter is to trap particles like dust, pollen, mold spores, and pet dander. When the filter is dirty and clogged, it can’t effectively capture these particles, leading to poorer indoor air quality. This can be particularly problematic for individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions.
- Overheating and Freezing: In a forced-air heating system, a dirty filter can cause the system to overheat and shut down as it struggles to circulate air. In an air conditioning system, a dirty filter can lead to freezing of the evaporator coils due to reduced airflow.
- HVAC System Damage: Over time, the strain of operating with a dirty filter can lead to wear and tear on your HVAC system. This can result in more frequent breakdowns and potentially costly repairs.
- Shortened Lifespan of Equipment: The extra strain on your HVAC system caused by a dirty filter can lead to premature wear and tear on critical components. This can shorten the overall lifespan of your heating and cooling equipment.
- Uneven Temperature Distribution: Reduced airflow due to a dirty filter can lead to uneven temperatures in different parts of your home. Some rooms may feel too hot while others may be too cold.
- Foul Odors: A dirty air filter can sometimes lead to unpleasant odors as trapped particles start to decompose.
- Reduced Comfort: With reduced airflow and potential temperature imbalances, you may find it harder to maintain a comfortable living environment.
- Increased Allergy and Asthma Symptoms: For individuals with allergies or asthma, poor indoor air quality can exacerbate symptoms. A dirty filter can allow more allergens to circulate in the air.
Symptoms you might experience due to a poorly maintained filter are:
- Worsening of allergies
- Frequent asthma attacks
- Respiratory and sinus infections
- Recurrent colds
- Watery eyes
- Repeated coughs and sneezing
- Dizziness and headaches
An unclean and clogged filter also cannot effectively remove humidity and humidity serve as a perfect environment to grow micro organism.
To prevent these issues, it’s important to regularly check and change your air filter according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. This simple maintenance task can help keep your HVAC system running efficiently and maintain good indoor air quality.
Where should you position a portable air cleaner in your home?
Where in your home to place a portable air cleaner to help protect from airborne infections depends on the situation. Put the air cleaner in the room where most people spend most of their time (e.g. a living room or bedroom) unless.
1. If an individual is in isolation due to an ongoing infection, it is advised to position the air cleaner in the area where they are isolating. Refer to the CDC’s isolation guidelines for individuals who have been exposed to COVID-19 for further information.
2.If there is a member of the household who is particularly susceptible to infection risks, it is recommended to position the air cleaner in the area where they predominantly spend their time.
Resources
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3165134/
https://acaai.org/allergies/management-treatment/living-with-allergies/air-filters/
https://medicalnewsbulletin.com/is-your-air-filter-making-you-sick/
https://www.epa.gov/coronavirus/air-cleaners-hvac-filters-and-coronavirus-covid-19
https://www.filtertime.com/news/what-is-the-meaning-of-mpr-fpr-and-merv#:~:text=